A whole house fan is a type of ventilation system that draws cool outdoor air into the home and exhausts warm indoor air through the attic and roof. It is designed to improve indoor air quality and reduce the need for air conditioning during mild weather conditions. The main advantages of a whole house fan include energy savings, improved indoor air quality, and enhanced comfort.
Advantages of a Whole House Fan:
Energy Savings: A whole house fan consumes much less energy than an air conditioner, making it a more cost-effective solution for cooling homes during mild weather conditions. By using a whole house fan to draw in cool outdoor air and exhaust warm indoor air, homeowners can reduce their energy bills by up to 50%.
Improved Indoor Air Quality: A whole house fan can improve indoor air quality by flushing out stale air, odors, and pollutants from the home. It can also help to reduce humidity levels, which can lead to mold and mildew growth.
Enhanced Comfort: A whole house fan can provide a natural and comfortable breeze throughout the home, creating a more pleasant living environment. It can also reduce the need for air conditioning during mild weather conditions, which can help to extend the lifespan of the air conditioning system.
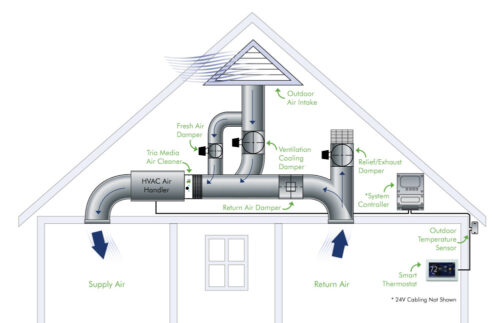 How a Whole House Fan Works:
How a Whole House Fan Works:
A whole house fan works by drawing cool outdoor air into the home through open windows or vents, and exhausting warm indoor air through the attic and roof. The fan is typically installed in the attic, where it can be connected to vents or ducts that lead to the living areas of the home.
When the fan is turned on, it creates negative pressure in the home, causing cool outdoor air to be drawn into the home and warm indoor air to be expelled through the attic and roof. This process can be enhanced by opening windows and doors to create a cross-breeze throughout the home.
The fan is typically operated using a wall-mounted switch or a timer, and it can be set to run for a specified period of time or continuously.
How a Whole House Fan is Installed:
Installing a whole house fan typically involves the following steps:
Determine the Size and Location of the Fan: The size of the fan should be chosen based on the square footage of the home, and the location of the fan should be chosen based on the attic space and available vents or ducts.
Prepare the Attic: The attic should be cleared of any debris and prepared for the installation of the fan. This may involve installing additional vents or ducts to improve ventilation.
Install the Fan: The fan should be installed in the designated location and connected to the appropriate vents or ducts. The electrical wiring should also be connected to a wall-mounted switch or timer.
Test and Balance the System: Once the fan is installed, it should be tested to ensure that it is functioning properly. The system should also be balanced to ensure that air is being drawn in evenly from all areas of the home.
Seal and Insulate: Finally, any gaps or leaks in the attic should be sealed to prevent air leakage, and the attic should be insulated to improve energy efficiency.
